Deaf, deaf and Hard of Hearing
On this page:

About Deaf, deaf and hard of hearing
The term “Deaf” (capitalised D) describes individuals who communicate using Australian Sign Language (Auslan). These individuals identify as belonging to the signing Deaf community, which is like a different ethnic group; it has its own language and culture. Deaf people often interact with both the Deaf and hearing communities, but do not consider themselves to be “hearing impaired”.
In contrast, the term “deaf” (lower case d) describes individuals who physically do not hear, as well as those who do not identify as members of the signing Deaf community.
“Hard of hearing” describes individuals who have a mild to moderate hearing loss, or who have developed hearing loss in late childhood or adulthood. People who are hard of hearing typically use spoken language (including lip-reading) to communicate. They may also rely on residual hearing (possibly with use of a hearing aid), written language, or gestures.
"Hearing impaired" is also often used in Australia to describe people who are hard of hearing, but this is generally not the preferred term.
Using the wrong word to describe a person’s hearing can be offensive, so it is important to ask the student and their family which group they identify with. For more information, see our inclusive language guide.

Strengths
What might be some strengths?
- Some students who are Deaf or hard of hearing can achieve similar results to their peers academically.
- Some students are strong visual learners, and are able to mentally hold and manipulate visual information (e.g. picture an object and rotate that picture in their mind).
- Deaf and hard of hearing students may also show a high level of resilience, especially in their determination to understand a concept, complete a task and master a skill.
Where might you provide support?
- Students who are Deaf or hard of hearing may need support understanding spoken instructions.
- Some students may have challenges with speech, vocabulary, attention and behaviour.
- Some Deaf or hard of hearing students may need support forming and maintaining peer relationships.

Evidence-based strategies
Consider adjustments to teaching style
Make adjustments to activities and equipment
Build communication skills
- Communicate in different ways. Consider including visual methods of communication, such as posters, role plays, captioned videos, storyboards and classroom schedules.
- Consider using a role model. Deaf and hard of hearing students who communicate via sign language may benefit from having a language role model that they can learn from and communicate with in the classroom. It may be helpful to work with an interpreter or learn some key Auslan signs.
- Check you have the student’s attention. When giving instructions or communicating with the student, maintain eye contact and check that the student can see your face and mouth.
- Allow more time to communicate. Some students may need more time to process information, especially if lip reading is involved, and answer questions (e.g. via the use of sign language, picture or gestures).
- Allow the student to use technology or assistive devices. Deaf and hard of hearing students may have different ways of communicating. Some might use assistive technologies such as hearing aids and cochlear implants, and may communicate using tablets, pictures or gestures. Consider how you can incorporate these into classroom activities.
- Maximise technology. Some students may have communication aids to assist with participation in the classroom. For example, a transmitter and microphone may be needed so students can pick up verbal communication. Encourage students to use technology that best supports them.
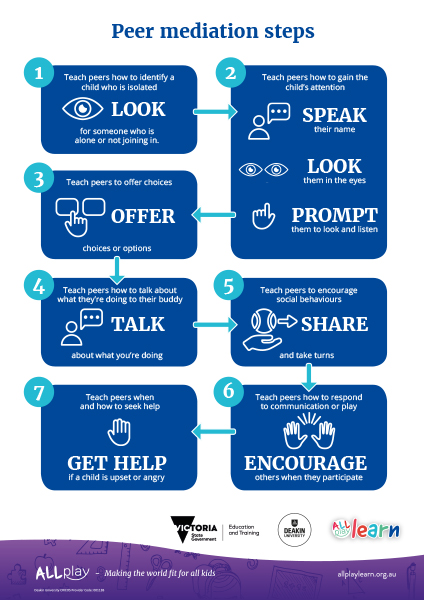
- Provide plenty of opportunities for peer interaction. Consider providing small group work, buddies and role playing. It may be helpful to teach hearing students how to best communicate with their Deaf, deaf and hard of hearing peers. This could involve teaching key Auslan signs to the classroom.
- Support learners to develop the skills needed to understand and solve interpersonal problems. For example, teach students how to apologise, share, cooperate and understand others’ perspectives. You can also teach students how to recognise and regulate their emotions. Use a combination of direct instruction, role playing, modelling, video modelling and stories.
- Self-video modelling. Have students record themselves performing a target behaviour or skill, and then watch the video to reinforce the correct actions.
- Articulation support. If communicating with a student using Auslan, sit beside the student, rather than across from them, to support perspective-taking and imitation.

Best practice tips
Consider the environment
Consider how you communicate and give instructions
Consider adjustments to activities
Encourage participation
Foster an inclusive and safe school environment
Promote self-determination
- Students may benefit from a text-rich environment. Consider including visual schedules and posters to illustrate key learning concepts and activities.
- The physical classroom space may need to be rearranged. This is so that students are positioned where they can easily see both you and their classmates. Encourage students to sit towards the front of the classroom and at an angle that works best for them.
- Check the classroom has plenty of light. That way the student can better see visual material and demonstrations. This will also help with lip-reading or if an interpreter is present. When communicating with the student, check that you are not standing directly in front of windows and light sources.
- Be aware of noise levels. Noisy environments may distract students who use hearing aids, cochlear implants and other assistive listening devices.
- Remove distractions. Students with communication disorders might be easily distracted by objects both inside and outside the classroom environment. Consider sitting the student away from, or with their back to, the windows.
- Change topics slowly. It may be helpful to pause before starting a new subject during classroom discussions. Consider explaining what is being discussed to the student, or providing brief clues.
- Check that you have the student’s attention. When giving instructions or communicating with the student, maintain eye contact and check that the student can see your face and mouth. It may be helpful (particularly for students who lip read) to avoid moving around the classroom when speaking.
- Consider speaking at a slower pace. This could help students who lip-read to understand what is being said. Try not to shout or exaggerate how slow you speak. Discuss with the student the pace that works best for them.
- Repeat and rephrase instruction. Some students may need instructions to be repeated. Consider how to present the information in a different and simpler way rather than repeat the same information in the same way.
- Check for understanding. Frequently check in with the student to see if they understand the tasks they need to complete. Consider how this can be done without the student feeling singled out.
- Consider how to get the student’s attention. Before speaking with the student, you may need to get their attention first. This might be through a slight touch on the shoulder or by standing close to them. Ask the student how they would like you to gain their attention.
- Consider providing written copies of lesson notes. This might be helpful for students who lip read. Consider providing notes or encouraging another student to assist with note taking.
- Check that online learning material is accessible. For example, ensure that video and audio content is high quality (e.g., limited background music, clear graphics) and that captioning is accurate and legible.
- Provide frequent rest breaks. Lip reading can take a lot of concentration, and some students may need breaks to manage fatigue.
- Equip students with the skills and supports to participate fully in class. This may include building students’ language and communication skills so they can participate in classroom discussions. Teaching students how to repair communication breakdowns and use interpreters effectively could be useful.
- Students who are Deaf or hard of hearing may be vulnerable to bullying. Encouraging peers to develop positive attitudes and respect towards diversity can be helpful. You can also teach students ways to be a prosocial bystander when they see somebody being bullied. Visit AllPlay Learn’s Inclusive Communities for Schools page to access a suite of resources to support you in building an inclusive school culture.
- Promote self-determination. Empower and teach children to make simple choices, set goals, be independent, and develop problem-solving abilities. Use technology as needed. For example, technology can be used by students to indicate preference.

Curriculum considerations
- The arts curriculum can provide Deaf and hard of hearing students with opportunities to freely express their passions, thinking, and emotions. It may also help with developing problem solving, movement, visual and social skills.
- Remember to consider the classroom environment.
- Visit AllPlay Dance for resources to support students who are Deaf, deaf and hard of hearing to be fully involved in dance activities.
- Some Deaf and hard of hearing students may need support with reading and writing as they may communicate primarily via sign language. Consider working with an Auslan interpreter.
- Phonological skills (i.e., phonemes, graphemes, morphemes, and orthography), phonics (e.g., understanding the relationship between phonemes and graphemes) may be important skills for students to master when learning to read. Use explicit phonic-based instruction and visual tools (e.g., Visual Phonics).
- When teaching the student new words or key literacy concepts, consider a multisensory and multimodal approach. Use a combination of objects, tactile activities and visual aids such as key cards, flip charts or videos alongside written and spoken and/or signed language.This can then be complemented by examples that the student can relate to.
- Consider making adjustments to your teaching style.
- Some Deaf and hard of hearing students may have trouble with their balance during physical activities.
- Consider how you communicate and give instruction.
- Consider our AllPlay Footy resources to support students who are Deaf, deaf and hard of hearing to be involved in footy.
- Consider adjusting your teaching style.
- Some Deaf and hard of hearing students may need to learn both spoken English and sign language (e.g. Auslan). This may make learning an additional language challenging.
- Assess whether learning a language will be of advantage to Deaf and hard of hearing students on a case-by-case basis. Work collaboratively with the student and their parents and support team.
- If they are learning a language, focus on areas of strengths (e.g. visual learning) and build from there.
- Some Deaf and hard of hearing students may need support with abstract mathematical concepts, attention and memory.
- Give clear, specific and direct instructions. It might be helpful to present maths problems in a step-by-step format.
- Consider using visual aids such as picture cards, flip charts or posters that students can refer to quickly and easily.
- Some students may need more time to learn and complete their tasks. Consider breaking down learning and activities into smaller but challenging concepts or tasks.
- Encourage the transfer of maths concepts into the student’s everyday activities. This can be through hands-on arts and craft activities, or role plays that focus on some of the language used in mathematics (e.g. more, less, if).
- Consider using computer software to support the student.
- Consider using hands-on activities that use multiple senses (e.g. touch, sight and smell) to reinforce key concepts.
- Think about how you communicate and give instruction and consider the environment.
- Some students might benefit from the use of videos and computer software to be able to visualise key learning concepts.
- Consider adjusting activities and equipment.

Other considerations
- Some Deaf and hard of hearing students may not know how to tell an adult if there is an emergency, or what to do in an emergency or emergency drill. Work collaboratively with the individual student and their parents/support team, to find out the best methods of communication and support.
- Consider how you can alert a student who is Deaf and hard of hearing, in the event of an emergency. Collaborate with the student, and their parents, regarding relevant signs, equipment, and strategies that can be used.
- It might be helpful to spend time discussing and practising what to do if an emergency occurs within the classroom. Role plays and demonstrations may help.
- Consider having a poster that shows the student the sequence of actions to undertake in the case of an emergency. Check that the student is aware of where this is, and is able to easily and frequently access this.
- Consider discussing with parents additional strategies for supporting the child with homework if needed.
- Provide plenty of opportunities for social interactions. Encourage classmates and other staff members to use some of the key communication methods used by the Deaf and hard of hearing student.
- If group work is being used, small group sizes can encourage participation and help Deaf and hard of hearing students follow discussions (e.g. via lip reading).
- See: Build socio-emotional skills, Encourage participation, and Foster an inclusive and safe school environment.
- Provide the student with information about the excursion/camp ahead of time. It might be useful to show them pictures of the destination so they know what to expect.
- Consider the excursion destination and the availability of visual information and captioned videos.
- Students who are Deaf or hard of hearing may benefit from supports when moving across education settings.
- Tell students what will be the same so that they know they already have some of the skills they will need.
- It may be helpful to teach and practice organisation and homework skills, and time- and self- management skills.
- For more information about supporting students with disabilities when transitioning to a primary or secondary school setting access AllPlay Learn's transition page.
- For children transitioning to primary school access AllPlay Learn's Story A school day, and for children transitioning to secondary school access Access AllPlay Learn’s story How to be Organised How to be organised
- Students who are Deaf, deaf and hard of hearing can sometimes also experience specific learning disability, blind or low vision, or attention and communication challenges.
- Refer to information about these areas to help support the student.
- Refer to the ABC approach for more information on how to reduce challenging behaviour by supporting the child and promoting more helpful behaviour, and our emotions page for more information about supporting a child with managing their emotions.

Relevant resources
Visit our resources page for a range of resources that can help to create inclusive education environments for children with disabilities and developmental challenges. Some particularly relevant resources for children who are Deaf, deaf and hard of hearing include: